- Community, Society
- No Comment
A quarter of rural Zimbabwean population defecate in the open, says official estimate
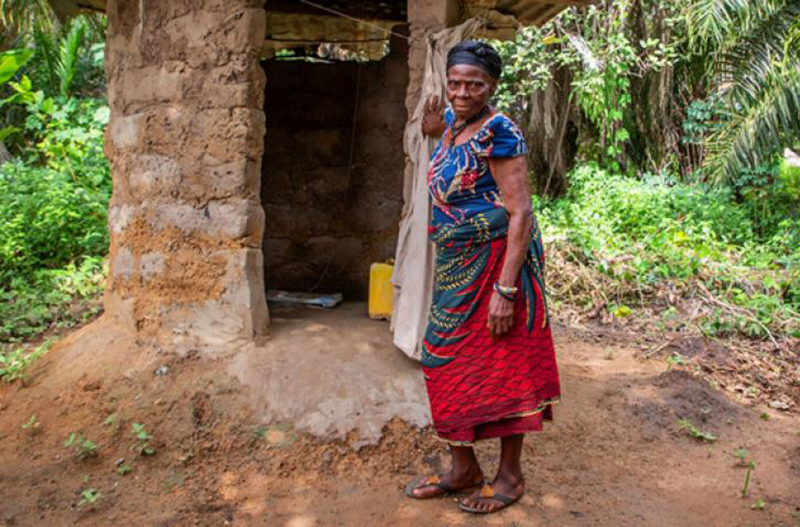
By News24
- One quarter of rural Zimbabweans have no access to ablution facilities at all, according to a new formal estimate.
- Where there are toilets, only 6% have water for hand washing.
- And about half of rural households have no access to basic water services.
HARARE: After some improvement, Zimbabwe has for the past five years held steady at about 25% of the rural population with no access to toilets, according to new official data.
That is down from 30% at the turn of the century.
But the numbers have not improved in some time, according to the latest Zimbabwe Livelihoods Assessment Committee (ZimLAC) report on rural livelihoods, chaired by the country’s Food and Nutrition Council.
About half of Zimbabwe’s rural population have access to basic toilets and another 9% have access to limited toilets. Others have toilets that have never been upgraded or improved.
That is only on average, however. Matabeleland North, one of the country’s most underdeveloped regions, has the worst open defecation rate at 50%, and within that province, one district, Binga, recorded a 73% rate of open defecation.
READ | City of eThekwini pays millions for a handful of useless toilets and showers
In Lupane, the provincial capital of Matabeleland North, 53% of residents have no access to toilets.
Last month, Nkayi, another area within Matabeleland North, benefitted from a five-year programme run by USAID to build toilets.
Before that, residents didn’t know the importance of having toilets, the local media reported.
“We took pride in going to the bush. As women here, we lacked knowledge on the importance of having a toilet at home,” one resident, Bahle Makhalima, told journalists.
While other provinces are better off, almost none have access to water after they use a toilet. According to the report, only 6% of households have hand washing stations.
ALSO READ | Africa under the microscope: Continent has 44 disease outbreaks and 104 active epidemic emergencies
When the rainy season – which is frequently marked by flooding – came to an end, waterborne illnesses spiked in Zimbabwe due to a lack of clean water in townships and corroded water lines.
In 2008, the country set an African record of 4 200 deaths due to cholera.
It is experiencing a continued cholera outbreak, joined between last year and this with cases in Malawi, Zambia, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Nigeria.
In many of those countries, people reported using open wells for drinking and cooking water.
At the level of overall basic water services, Zimbabwe has gone backwards in the past year, said ZimLAC, with the level of access declining from 60% in 2023 to 52% in 2024.
